BofA Global Research analyst compares their short- and long-term prospects.

At a Glance
- Microsoft wins the week but Google should prevail in the long run.
- Google's key advantage: Mobile distribution as the default iOS search engine plus Android.
- A 1-point gain in search market share could add $2 billion to Microsoft's revenue.
Microsoft and Google are in the throes of a throwdown over generative AI.
During dueling events this week, Google showed off its ChatGPT rival, Bard, and unveiled plans to make Search generate more conversation-like results, along with updates to Lens and Maps. Meanwhile, Microsoft announced it was incorporating ChatGPT into Bing and Edge, initially with a limited public preview.
"Microsoft won the week, with better product strategy and demos, while Google's presentation felt reactive with little new news, and even included an inaccurate AI chatbot response," wrote BofA Global Research analyst Justin Post, in a Feb. 9 research note shared with AI Business.
In its opening gambit, Microsoft has "made it clear that the company sees an opening in search" and a one-point gain in search share "could drive an additional $2 billion in revenue," the analyst said.
However, "we see both product and distribution advantages for Google search," he added. "We think Google likely has leading AI technology." Also, its "big reveal is still to come."
Google might see a short-term hit, but Post believes the search giant should prevail in the long run due to the following advantages:
Google has been preparing for years and likely has superior AI tech for search or at least better data to drive better results.
Google's language models are highly capable.
Google has extensive computing infrastructure to build on.
Google search has a large distribution advantage with iOS and Android.
Google has room to spend more on AI search since its 2023 capital spending plan showed no increase from last year.
The landscape
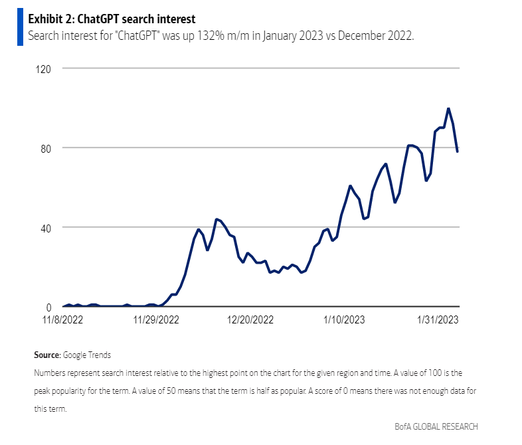
ChatGPT is a big hit: It had a billion cumulative web visits since its debut in November. Post expects the chatbot and Bing to see an uptick in interest, ahead of Google's full launch. He said searches for ChatGPT rose 132% in January from the prior month, building on three months of rapid increases.
2. Bing mobile app downloads jumped 66% to 29,300 on the day of Microsoft's AI event, up from 17,700 a day earlier. However, it remains far below Google's 342,000. Notably, Google app downloads rose 4% on the day of Microsoft's event.
3. Microsoft moved first to incorporate generative AI into its search engine and open it to the public in limited preview.
4. AI-based queries are not cheap. ChatGPT is hosted on Azure and Microsoft charges $3 an hour for a single A100 GPU, and each word generated on ChatGPT costs $0.0003, said Post, citing Indian Express. A ChatGPT response is usually at least 30 words, so it would cost at least 1 cent. But an AI-powered cost per query could be 2 cents to 3 cents higher, although it should moderate over time.
Impact to Google
Will Bing have better search results after incorporating AI? Not likely. Google has both a data and learning advantage but Microsoft could close the gap in search quality.
Will Bing hurt Google's market share? Probably for only a few weeks. Google Search market share is 92% vs. Bing's 3% to 4%. Since more than 50% of these searches are done on a mobile device, Google's distribution on iOS (as the default search engine) and Android means "little change in search market share" over the longer term.
How will AI-enabled search affect costs? Google could see search costs go up by $12 billion (1.2 trillion searches at a penny per query) - or 5% of 2023 revenue.
LaMDA vs. ChatGPT
Both language models are based on GPT-3.5 but “their approaches to training are very different,” Post said. LaMDA is a supervised-learning model that was trained using dialogue data that generates responses that are “more human-natured” than those of ChatGPT, he wrote.
ChatGPT is a pre-trained model that is based on web pages and generates responses from “reliable” outside sources, Post explained.
As a result, LaMDA can foster a “more organic flow of dialogue” while ChatGPT has “extensive training in web writing, making it well suited for deciphering complex grammatical structures and responding to queries,” the analyst said.
That means LaMDA is better for users looking for a conversational chatbot while ChatGPT should be the choice for a Q&A or to conduct research.
This article has been updated to reflect new comments from the analyst.
Read more about:
ChatGPT / Generative AIAbout the Author(s)
You May Also Like


.jpg?width=700&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=700&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=700&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)


.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)

.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)