The LLM can generate responses in a way ChatGPT can’t
.jpg?width=850&auto=webp&quality=95&format=jpg&disable=upscale)
At a Glance
- Meta has showcased a language model that can use multiple external software tools to generate responses to NLP inputs.
- Toolformer uses search engines and machine translation tools to create outputs that surpass OpenAI's GPT-3.
AI researchers at Facebook parent Meta have unveiled Toolformer, a new language model designed to handle multiple API calls for natural language processing use cases.
Toolformer is based on GPT-J, a 6.7 billion-parameter open-source language model. Meta’s researchers equipped the model with a range of tools, which it can autonomously use to achieve tasks, like predicting text or answering math questions.
The tools Toolformer has access to include a calculator, a Q&A system, two different search engines, a machine translation system and a calendar.
The machine translation system used is a 600 million-parameter version of its NLLB model which works for 200 languages. Toolformer uses a calendar API that, when queried, returns the current date without taking any input. For answering questions, the system uses Meta’s Atlas model.
Notably one of its search engines is Wikipedia Search, which returns short text snippets from Wikipedia when prompted. The use of Wikipedia however has been criticized for its reliability. Anyone can edit Wikipedia, with even the platform itself acknowledging that it is “not a reliable source for citations.”
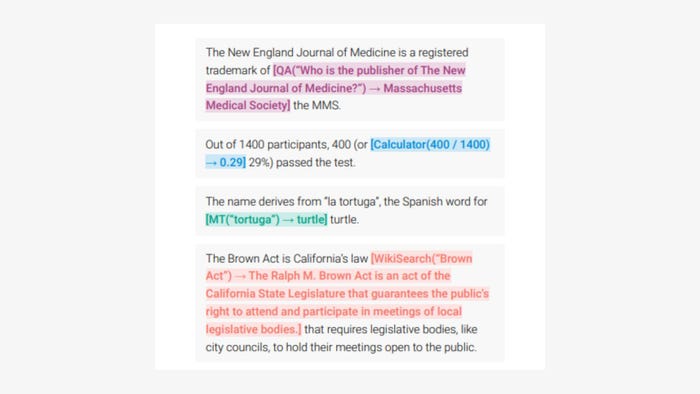
The above example showcases Toolformer’s capabilities. The model autonomously decides to call different APIs to obtain information useful for completing a piece of text. This example from Meta’s paper sees the model utilize a question-answering system, a calculator, a machine translation system and a Wikipedia search engine.
.jpg?width=700&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
Despite the underlying model being based on a GPT-2 model, Meta found that Toolformer can outperform the larger GPT-3 model on a handful of zero-shot NLP tasks. While GPT-3 performed better on question answering, Toolformer defeated the OpenAI model on most other tests, including mathematical reasoning and machine translation.
Toolformer is similar to OpenAI’s ChatGPT, in that a user inputs natural language prompts and the system generates a response. Toolformer differs, however, in that its various tools can be used to generate responses based on recent events with tools like the search engine function. ChatGPT and others are built using datasets that only go up to a certain point, meaning they cannot respond to user queries on recent events.
Toolformer is more incomplete than its ChatGPT contemporary, with Meta’s researchers acknowledging in their paper there are “clear limitations to what can be achieved” with its current method in its current form.
“Our current approach also does not allow the language model to use a tool in an interactive way – especially for tools such as search engines, that could potentially return hundreds of different results, enabling a language model to browse through these results or to refine its search query,” the paper reads.
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like


.jpg?width=700&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=700&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=700&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)

