Intel Unveils AI Chips for Enhanced Performance at Vision 2024 Event
Intel claims its new Gaudi 3 AI accelerators outpower Nvidia’s flagship GPUs “at a fraction of the cost” at Vision 2024
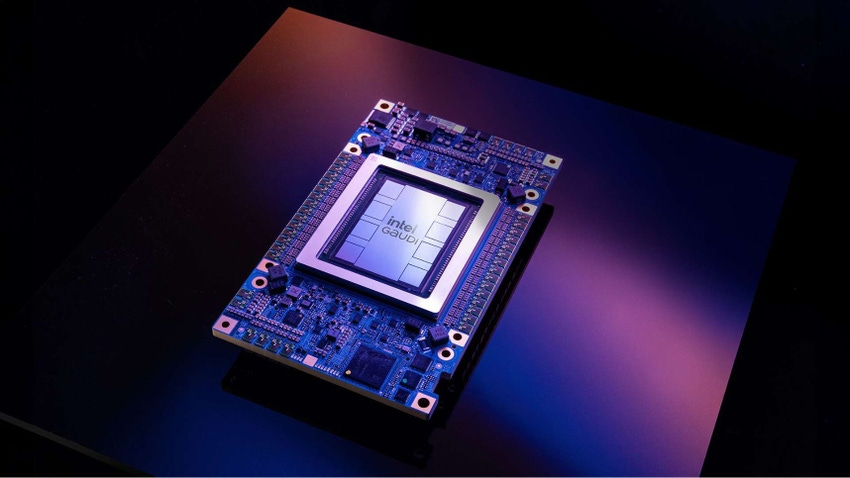
Intel unveiled its latest AI chips, Gaudi 3, designed to offer increased performance training and running large language models at Intel Vision 2024 in Phoenix, Arizona this week.
The new hardware is designed to power cloud-based infrastructure for training and inferencing large language models.
Intel claims the new hardware is 50% faster at training and 30% faster in processing large language models compared to Nvidia’s H100 GPUs.
“Innovation is advancing at an unprecedented pace, all enabled by silicon – and every company is quickly becoming an AI company,” said Intel CEO Pat Gelsinger. “Intel is bringing AI everywhere across the enterprise, from the PC to the data center to the edge. Our latest Gaudi, Xeon and Core Ultra platforms are delivering a cohesive set of flexible solutions tailored to meet the changing needs of our customers and partners and capitalize on the immense opportunities ahead.”
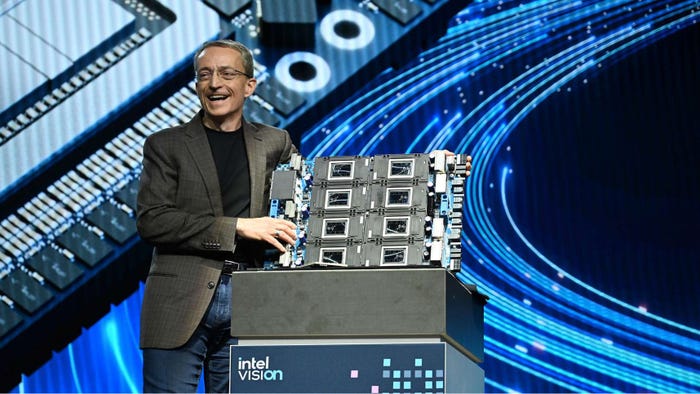
Intel CEO Pat Gelsinger with eight interconnected Gaudi 3s | Credit: Intel
The new hardware boasts increased memory and networking bandwidth and provides four times the AI compute compared to the prior Gaudi 2s. The chips house tens of thousands of accelerators and can be interconnected via Ethernet.
Intel said the Gaudi 3 chips' cost-effectiveness makes them suitable for enterprises running experiments or scaling existing AI deployments. Enterprise customers can use the chips to scale their efforts from a single node to clusters to support their AI workloads.
“In the ever-evolving landscape of the AI market, a significant gap persists in the current offerings. Feedback from our customers and the broader market underscores a desire for increased choice,” said Justin Hotard, Intel executive vice president and general manager of its data center and AI group.
“Enterprises weigh considerations such as availability, scalability, performance, cost, and energy efficiency. Intel Gaudi 3 stands out as the generative AI alternative presenting a compelling combination of price performance, system scalability, and time-to-value advantage.”
South Korean internet provider Naver is among the early adopters. At Vision 2024, the company announced it is using the new Gaudi hardware to power new large language models for its global AI services.
Intel’s Gaudi 3 chips will be available in the second half of 2024 to hardware manufacturers including Dell Technologies, HPE and Lenovo before a general release later this year.
A PCIe add-in card for the Gaudi 3, which allows users to connect other high-speed input-output components like Wi-Fi cards or SSDs, will also launch in Q3 2024.
Alongside Gaudi 3, Intel provided a glimpse at its new Xeon processors.
The Xeon 6s, built to power generative AI workloads, can run in data centers for cloud and edge workloads.
Intel unveiled two Xeon 6 product lines, Sierra Forest and Granite Rapids, which will launch later this year.

Gelsinger shows off the new Sierra Forest and Granite Rapids Xeon processes | Credit: Intel
The Xeon 6 processors will replace the 5th gen versions, which were only rolled out earlier this year.
Additionally, Intel unveiled Tiber, a suite of solutions businesses can use to ease generative AI software deployments.
Tiber compiles tools enterprise customers can use to securely roll out AI services in the cloud or at the edge. Tiber will be released in the coming months.
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like


.jpg?width=700&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=700&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=700&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)