DALL-E 3 is Now Available for ChatGPT Plus, Enterprise Users
Enhanced training gives OpenAI’s image-generation model, DALL-E 3, more powerful capabilities

At a Glance
- DALL-E 3, OpenAI’s latest AI image generation model, is now available to ChatGPT Plus and Enterprise users.
- Enhanced training makes DALL-E 3 more powerful than DALL-E 2 and rival Stable Diffusion XL.
- OpenAI also reveals more details of DALL-E 3 - but not much more.
OpenAI’s most powerful image-generation model, DALL-E 3, is now available for ChatGPT Plus and Enterprise subscribers.
First glimpsed in late September, the AI image generation model’s latest version improves upon its training data quality through highly descriptive image captions.
In a new paper from OpenAI outlining how they built DALL-E 3, OpenAI’s researchers contend that previous text-to-image models struggled due to “noisy and inaccurate” image captions in datasets.
When building DALL-E 3, OpenAI built a dedicated image captioning system that generates highly descriptive captions for images. The captions would describe details in the images like objects, colors and textures. Following the introduction of improved captions, the new DALL-E would return images in response to prompts that were of far greater quality than prior image generation models, according to OpenAI researchers.
DALL-E 3 is trained on 95% synthetic descriptive captions and yet outperforms DALL-E 2 and Stable Diffusion XL when it comes to tests covering prompt following, coherence and aesthetics. The new image generation model even performs better when given expanded captions from a language model like GPT-4, since it is trained on detailed captions.
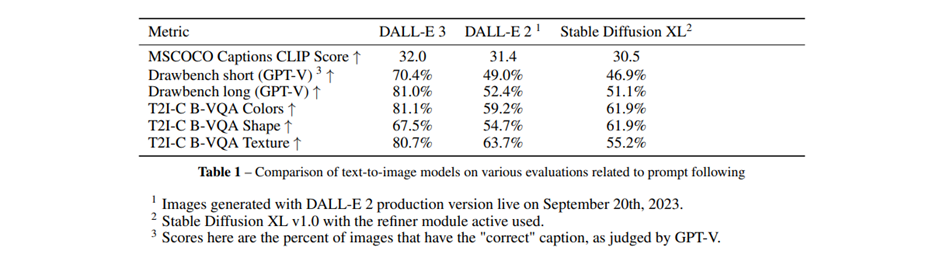
Credit: OpenAI
More accurate prompt following
DALL-E 3’s improved image captioning system means it can follow prompts better and understands more nuance from inputs.

DALL-E 3 relies less on "prior knowledge" compared to DALL-E 2 and focuses more on the given prompt, resulting in more control of the desired output.
DALL-3 even produces significant improvements compared to DALL-E 2 when using the same prompt. Check out the below examples using the prompt “An expressive oil painting of a basketball player dunking, depicted as an explosion of a nebula.”
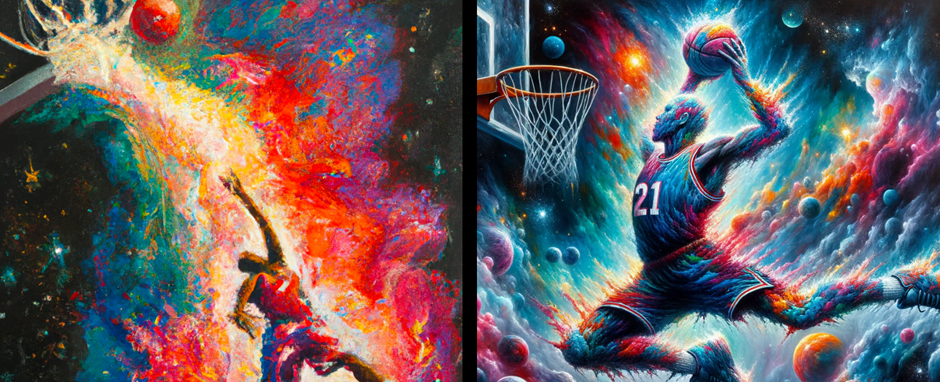
From left: DALL-E 2 image, DALL-E 3 image Credit: OpenAI
One major upgrade with regard to prompts is the model's ability to say no to potentially deviant inputs.
Previously, DALL-E 2 was designed to reject certain prompts. However, users were able to easily circumvent this – with researchers even able to generate ‘fake news’ content using the model.
OpenAI has sought to rectify this with DALL-E 3, imposing a far harsher wall on naughty prompts.
For example, DALL-E 3 now declines requests that ask for a public figure by name and will not generate images in the style of living artists.
The model is also stricter at declining requests when users ask it to generate violent, adult or hateful content. When building the model, OpenAI employed red teamers to try and circumvent the model to identify its weaknesses to shore it up before public release.
ChatGPT integration
Unlike other image generation systems, OpenAI sought to change the game with DALL-E 3, with the model now integrated directly into ChatGPT.
Users can input a prompt about a concept, and the model will generate a text response and ask the user if they would like images of that – creating a more seamless workflow experience.
OpenAI is positioning ChatGPT as a more multimodal experience, with new ways to interact with the chatbot via images and voice.
By building DALL-E 3 natively into ChatGPT, OpenAI created another way for users to interact with the bot. You can use ChatGPT to interact with DALL-E using natural language − and instead of tailing a prompt, use only certain phrases when inputting what image you want. Now users can ask ChatGPT in natural language to further refine an image until they get the correct putout.
A ‘significant’ step forward – but struggles remain
OpenAI’s paper describes DALL-E 3 as “a significant step forward” but some issues are still present.
For example, the new image generation model still struggles with object placement and spatial awareness. For example, using words like 'underneath' or 'behind' results in unreliable placement of objects in generated outputs. The team behind it says the problem is caused by the model's synthetic captioner, used to create the detailed captions it runs on. The tool is "unreliable at stating object placement," according to the paper.
Stay updated. Subscribe to the AI Business newsletter.
DALL-E 3 also suffers from issues stemming from its text encoder getting confused by missing or extra characters in the AI-generated captions used in its image training dataset. The paper reads: “When the model encounters text in a prompt, it actually sees tokens that represent whole words and must map those to letters in an image.”
Synthetic captions also can hallucinate details about an image, a botanical drawing of a flower could see the system hallucinate the plant's genus and species and put it in the caption, even when these details are available in text form in the image. This could impact DALL-E 3's ability to generate imagery for specific terms.
A hint of more transparency
The publication of the DALL-E 3 marks somewhat of a shift for OpenAI towards being a bit more transparent with its AI models.
Since its release of GPT-4, OpenAI has shifted its approach from being open about the parameters of its AI models to completely shutting off, restricting the flow of information on how its models were built, compared to rivals like Meta that are pushing for a more open source focused approach.
With the published paper on DALL-E 3 and the model card for GPT-4V, it shows OpenAI opening a glimpse into how its new models are made.
Add to that some specific features of the new model, including an opt-out form so creators can have their images removed from future image generation models from OpenAI.
The company has been researching ways of detecting AI-generated content. With DALL-E 3, OpenAI said it is working on ways to identify when an image was created with AI. This includes a new tool called a provenance classifier that can identify whether an image was generated by DALL-E 3. Though not much more is known – more information is expected soon.
However, a glimpse is all OpenAI is giving. The exact size of DALL-E 3 is unknown, nor is there access to the underlying source code. It also is not free, at least for now. There is currently one free way of accessing DALL-E 3: via Bing Image Creator with a Microsoft email. Such a move comes as a result of OpenAI’s strategic alignment with Microsoft.
Read more about:
ChatGPT / Generative AIAbout the Author(s)
You May Also Like


.jpg?width=700&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=700&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=700&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)

.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)