The 'Remarkable' AI Model Behind ChatGPT’s New Multimodal Powers
The rise of large multimodal models: GPT-4V can count objects, parse tables and text, perform in-context learning and is code-conditioned on visual inputs
.png?width=850&auto=webp&quality=95&format=jpg&disable=upscale)
At a Glance
- OpenAI gives Microsoft scientists access to GPT-4V, the multimodal model powering ChatGPT’s new voice and image capabilities.
- They found that GPT-4V has an "unprecedented" ability to process multimodal inputs, like an image with text written on it.
- It can read numbers on a table, analyze CT scans and interpret what's funny in an image.
Coming up to a year since ChatGPT’s release, OpenAI has greatly revamped the language model by giving it new image generation capabilities via DALL-E 3 and access to real-time information through Bing. But its new voice and image capabilities are arguably the most significant upgrade, potentially changing the way users interact with it.
ChatGPT is powered by a multitude of underlying systems – the newest of which is GPT-4V, or GPT-4 Vision, which gives it multimodal capabilities. Since the model's publication in late September, researchers from Microsoft, OpenAI’s largest investor and partner, ran a series of tests to assess its capabilities. They found that it shows "remarkable capabilities, some of which have not been investigated or demonstrated in existing approaches," according to their paper, ‘The Dawn of LMMs: Preliminary Explorations with GPT-4V(ision).’
They describe GPT-4V as a “powerful" model with an "unprecedented ability in processing arbitrarily interleaved multimodal inputs." Interleaved refers to interwoven assets, such as an image of a menu with a text list of entrees. GPT-4V can handle both simultaneously.
What is GPT-4V?
GPT-4V(ision) is a multimodal AI model developed by OpenAI. It allows a ChatGPT user to ask questions of an uploaded image, a process called visual question answering (VQA). Coming in October, GPT-4V's capabilities can be accessed via ChatGPT on the desktop or the iOS app version for subscribers to the $20-a-month ChatGPT Plus or the Enterprise version.
What can GPT-4V do?
GPT-4V can analyze interleaved text and images.

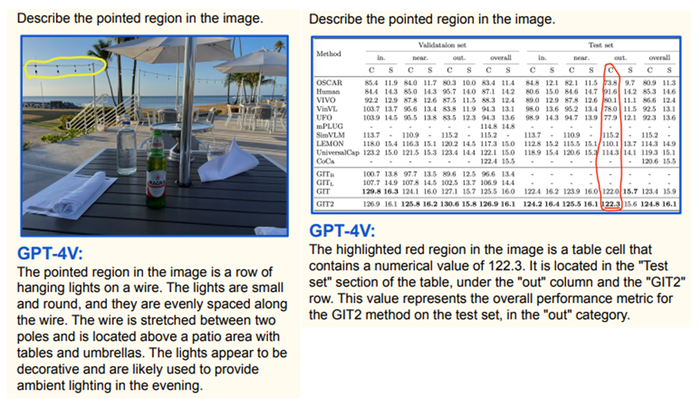
It can read highlights in images, including numbers in a table.
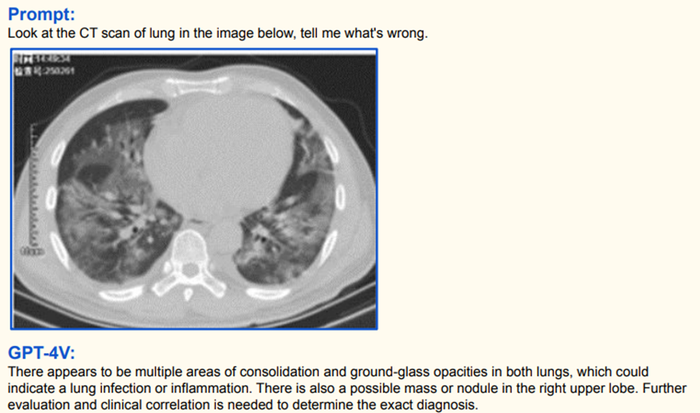
It can analyze medical images.
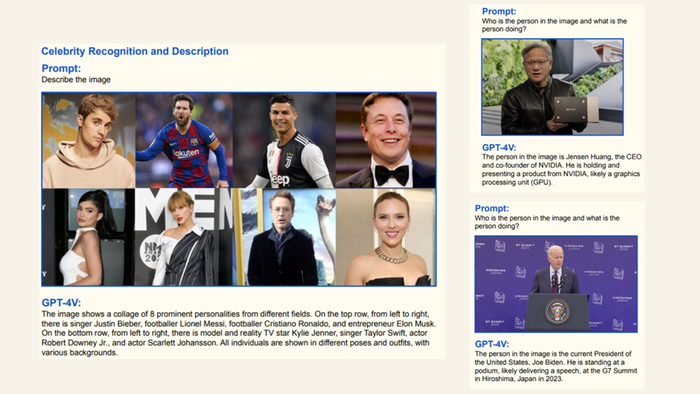
It can identify and describe the content of images.

The model can also understand scenes, such as a view of a road from a car dashboard camera and answer related questions. It can correctly identify celebrities such as football stars Lionel Messi or Cristiano Ronaldo.
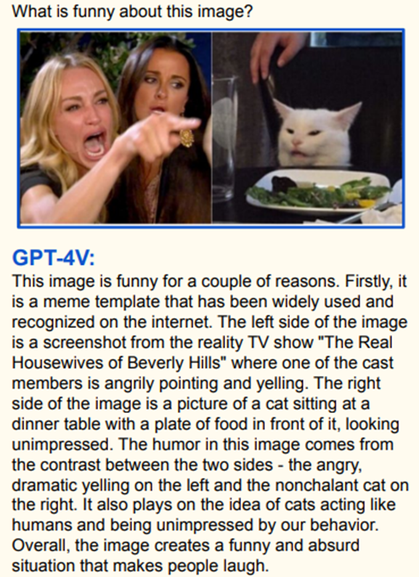
It can explain humor in memes.
The model can also generate detailed and coherent open-ended descriptions of image contents, going beyond just labels. It shows the ability for compositional reasoning, e.g. answering questions by locating relevant visual evidence.
GPT-4V’s key capabilities are the following:
Visual Reasoning: The model is able to comprehend visual relationships and contextual nuances beyond just labeling objects. It can answer questions by reasoning about an image, handle counterfactuals and novel scenarios.
Instruction Following: The model can follow textual instructions to perform new vision-language tasks without any parameter updates.
In-context Learning: GPT-4V exhibits in-context few-shot learning capacity, meaning it can adapt to new tasks given just a few demonstrations at the time of testing.
Visual Referring: The model understands visual pointers like arrows, and boxes directly overlaid on images to follow instructions.
Dense Captioning: GPT-4V generates detailed multi-sentence descriptions of image contents and their relationships.
Counting: GPT-4V can count instances of objects in an image based on a query.
Coding: The model shows an ability to generate code (e.g. JSON parsing) conditioned on visual inputs.
The model exhibits significantly enhanced vision-language understanding compared to prior multimodal models, according to the Microsoft scientists.
What are GPT-4V’s limitations?
Like every AI model before it, GPT-4V has its limitations.
For example, those hoping to use it for overtly complex use cases may find it difficult for the system to engage with specifically designed prompts.
GPT-4V's performance may not generalize well to new or unseen samples, and some complex cases may only work with specifically designed prompts.
The rise of large multimodal models (LMMs)
Multimodal AI models represent the next step in AI’s evolution. Text-generation models are now augmented with the ability to interact with more versatility through multimodality especially vision, since using an image as a prompt makes it easier for the user to query the model instead of awkwardly explaining a problem.
A sharply intelligent and multimodal ChatGPT brings OpenAI closer to creating artificial general intelligence (AGI), which is the startup’s ultimate goal and the Holy Grail of the AI community for decades. OpenAI said it seeks to develop AGI that is beneficial and safe for humanity - governments are crafting regulations to ensure it.
OpenAI is not the only one researching multimodal AI. Meta's army of researchers, led by Turing award winner Yann LeCun, has been publishing multimodal AI models to power the company’s vision of creating a metaverse universe for all. The likes of SeamlessM4T, AudioCraft and Voicebox will all work towards LeCun’s idea that multimodality will provide an advantage to AI users who want to be creative but lack technical skills.
Multimodal models also are a focus of research for next-gen foundation models at the recently formed Frontier Model Forum – made up of major AI developers including OpenAI, Microsoft, Google and Anthropic.
Read more about:
ChatGPT / Generative AIAbout the Author(s)
You May Also Like


.jpg?width=700&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=700&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=700&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)

.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)