OpenAI Unveils GPT-4 and Plans to Add it to ChatGPT+
OpenAI keeps quiet on GPT-4 size to potentially avoid giving away trade secrets
.jpg?width=850&auto=webp&quality=95&format=jpg&disable=upscale)
At a Glance
- OpenAI officially unveils GPT-4, its next-generation AI language model
- GPT-4 offers improved coding generation, image input capabilities and can even pass law exams
- GPT-4 is set to power ChatGPT+, OpenAI’s premium subscription service for its generative AI chatbot
After weeks of speculation, OpenAI has finally unveiled GPT-4, its latest and potentially biggest language model to date.
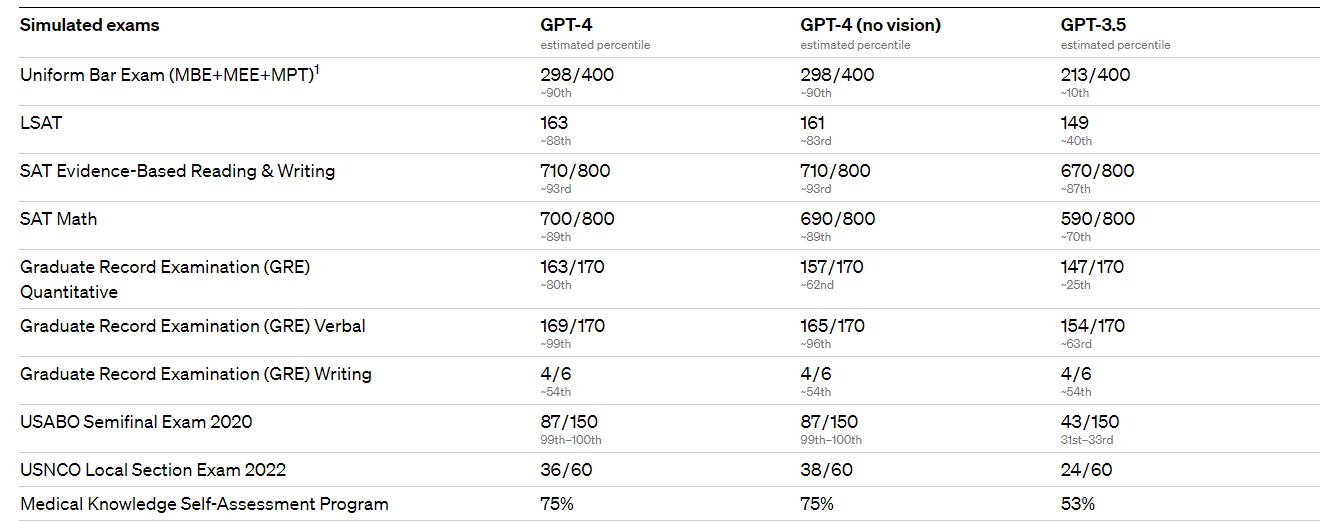
GPT-4 can accept images and text inputs and generate text outputs. According to OpenAI, GPT-4 “exhibits human-level performance,” with its creators claiming that GPT-4 passed a simulated bar exam with a score around the top 10% of test takers.
OpenAI CEO Sam Altman said GPT-4 is “still flawed, still limited, and it still seems more impressive on first use than it does after you spend more time with it.”
GPT-4 supersedes GPT-3, released in 2020 and GPT-3.5, one of the models used to fine-tune ChatGPT.
To create its latest model, OpenAI rebuilt its entire deep learning stack and co-designed a supercomputer with Microsoft to run the workloads. GPT-3.5 was used to test the system. The learnings from those tests enable OpenAI’s GPT-4 training run to be “unprecedentedly stable,” the company said.
Similar to previous GPT models, GPT-4 was trained to predict the next word in a document. The model was trained on publicly available data from the Internet as well as data OpenAI licensed from partners. The model was fine-tuned using reinforcement learning with human feedback (RLHF) so that generated responses to prompts align with the user’s intent.
Like ChatGPT, GPT-4 only knows about events up until September 2021 and does not learn from its experience.
And while OpenAI touts GPT-4 as being larger than previous models, it has opted to not reveal GPT-4's exact size. Parameters are used to determine a language model’s size. GPT-3 boasted 175 billion parameters. But size doesn’t always correlate to better performance. Google’s recently released LLaMA, for example, which comes in sizes ranging from seven billion parameters up to 65 billion parameters, with the 13 billion parameter version outperforming OpenAI’s GPT-3 “on most benchmarks” despite offering 162 billion parameters fewer.
OpenAI has revealed few technical specifications on GPT-4, offering no details on the exact data used or size details. When checking GPT-4’s performance in machine learning tests like MMLU (for more on that, read on), it lists little to no technical specs.
While OpenAI has not openly commented on the fact that it has changed course with its decision to keep details quiet, it could be to do with its increasing amounts of enterprise collaborations and partnerships. Following the launch of ChatGPT, OpenAI has received significant backing from Microsoft in exchange for partnering on language model tests, as well as agreements with Salesforce and Bain & Co., among others, meaning it may not want to give too much away over fears of leaking corporate secrets.
How can I get access to GPT-4?
Users can get their hands on GPT-4 via the soon-to-be-released ChatGPT+, a subscription-based service for those that want priority access and faster generations. OpenAI said it would adjust the exact usage cap for GPT-4 via ChatGPT+ depending on demand and system performance, but it expects capacity to be “severely constrained” at first, with plans to scale up over time.
To mitigate the constrained capacity, OpenAI said it may introduce a new subscription level for higher-volume GPT-4 usage. The company said: “We also hope at some point to offer some amount of free GPT-4 queries so those without a subscription can try it too.”
Bradley Shimmin, chief AI and data analytics analyst at Omdia, notes that ChatGPT will improve via the introduction of the new model, but won’t be drastically altered beyond generating more text and handling multiple modalities.
“Like GPT 3.5 before it and GPT-3 before that, ChatGPT running on the OpenAI GPT-4 model will, as OpenAI itself has stated, ‘turbocharge’ or ‘amplify’ what we could do before... to the tune of eight times more words and an understanding of images.
“But like before, the data used to train GPT-4 ended late last year, so like its predecessors, GPT-4 will not serve as your daily news feed.”
GPT-4 will also be available via an API, but only the text input iteration. To access the API, users have to sign up for the GPT-4 waitlist.
Developers will be given invited access to GPT-4 so OpenAI can test the balance between capacity with demand. Researchers studying the societal impact of AI or AI alignment issues can apply for subsidized access via OpenAI’s Researcher Access Program.
Company CEO Sam Altman said that the API will allow developers to significantly customize behavior, with the same function coming “soon” to ChatGPT.
Altman said that visual inputs for GPT-4 have only been previewed as the company needs time to "mitigate the safety challenges.”
To prepare the image input capability for wider availability, OpenAI said it is “collaborating closely” with a sole partner, Be My Eyes. The Be My Eyes Virtual Volunteer app will receive an image-to-text generator powered by GPT-4. Users can send images via the app, which will provide identification, interpretation and conversational visual assistance for a wide variety of tasks.
OpenAI announced it’s also open-sourcing OpenAI Evals, its framework for automated evaluation of AI model performance to allow developers to report potential shortcomings in its models.
How much does GPT-4 cost?
Pricing for GPT-4 is $0.03 per 1,000 prompt tokens and $0.06 per 1,000 completion tokens. Default rate limits are 40 1,000 tokens per minute and 200 requests per minute. Note, that GPT-4 has a context length of 8,192 tokens.
OpenAI is also providing limited access to its 32,768–context version, GPT-4-32k. Pricing for the larger model is $0.06 per 1,000 prompt tokens and $0.12 per 1,000 completion tokens.
Capabilities: What can GPT-4 do?
For casual conversations, OpenAI said there were "subtle" differences between GPT-3.5 and GPT-4. The wider differences come from GPT-4's reality and ability to be creative, compared to the previous model which was more focused on handling nuanced instructions.
GPT-4 outperformed GPT 3.5 on a host of simulated exams, including the Law School Admission Test, AP biology and the Uniform Bar Exam, among others.
GPT-4 was evaluated on several machine learning model benchmarks, including MMLU, HumanEval and DROP.
OpenAI contends that GPT-4 “considerably outperforms existing large language models.”
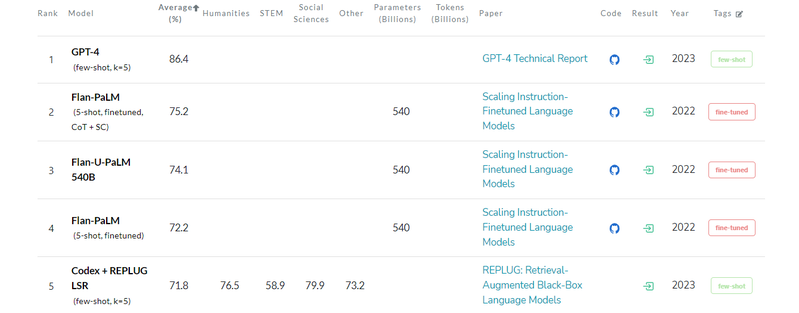
GPT-4 beat DeepMind’s Chinchilla and Gopher, as well as Google Flan-PaLM at multi-task language understanding. The test spans 14,000 multiple-choice problems in a variety of languages. In the 24 of 26 languages tested, GPT-4 rival models in English as well as low-resource languages such as Latvian, Welsh and Swahili.
Internally, OpenAI revealed it has been using GPT-4 to support sales and content moderation.
The model can also generate code and does so better than ChatGPT, which could open up an avenue for commercial exploitation, according to Dr. Andrew Rogoyski from the Institute for People-Centred AI at the University of Surrey.
“Imagine just having to ask your computer to create a program that, for example, predicts how your latest product will perform in its market. No programming is required. This could be transformational for many businesses,” said Dr. Rogoyski.
He noted that buried in the paper outlining GPT-4 is the comment, “we expect GPT-4 to impact even jobs that have historically required years of experience and education, such as legal services.” Such a comment could “send a chill up the spines of legal firms worldwide,” Rogoyski added.
GPT-4 Limitations
Despite being potentially OpenAI’s most advanced language model to date, GPT-4 retains the flaws present in its predecessors: it’s not fully reliable.
The model still generates false facts, something OpenAI describes as “hallucinates” and makes reasoning errors.
According to its creators, GPT-4 significantly reduces hallucinations relative to previous models, scoring 40% higher than GPT-3.5 on OpenAI’s internal adversarial factuality evaluations. GPT-4 recorded OpenAI’s best score on the TruthfulQA benchmark, which tests a model’s ability to separate fact from an adversarially-selected set of incorrect statements. The base GPT-4 model only scored slightly higher than GPT-3.5 on TruthfulQA. But after some RLHF post-training, the gap improved, with the model resisting common sayings but still missing subtle details.
OpenAI stressed that “great care” should be taken when using language model outputs, “particularly in high-stakes contexts.” The research team encouraged potential users to have humans review output, ground responses with additional context, or avoid high-stakes uses altogether.
The OpenAI team said it’s trying to make GPT-4 safer and more aligned from the beginning of training, compared to previous models, with efforts including selection and filtering of the pretraining data, evaluations and expert engagement and introducing model safety improvements over time.
OpenAI said it consulted over 50 experts on AI risks, cybersecurity and international security to adversarially test the model. Feedback from the experts fed into the model's improvements, the research team said, such as additional data to improve GPT-4's ability to refuse requests on how to synthesize dangerous chemicals.
Omdia’s Shimmin notes that OpenAI’s success with GPT-4 stems from the team building on prior knowledge.
He said: “(OpenAI) appears to be taking what allowed ChatGPT to escape the embarrassment of Microsoft Bing chatbot through the application of human-derived guardrails to help users avoid issues like adversarial usage, unwanted content and privacy concerns.
“This continued emphasis on safety and usability to me means more than the inevitable march of output tokens or multi-modal understanding – both of which can be had using a wide array of models that are now in the market, like Google PaLM.”
GPT-4 also has an additional safety reward signal during RLHF training to reduce harmful outputs, with the model trained to refuse toxic requests. The model was reportedly trained to prevent it from refusing valid requests.
“Our mitigations have significantly improved many of GPT-4’s safety properties compared to GPT-3.5,” OpenAI said. “We’ve decreased the model’s tendency to respond to requests for disallowed content by 82% compared to GPT-3.5, and GPT-4 responds to sensitive requests like medical advice and self-harm, in accordance with our policies 29% more often.”
The research team did however acknowledge that jailbreaks, where users circumvent language models so it generates responses outside of its guidelines, “still exist.” Users have routinely found ways to get around ChatGPT’s safety guardrails. OpenAI said that the best way to manage this limitation, for now, is with deployment-time safety techniques like monitoring for abuse.
Read more about:
ChatGPT / Generative AIAbout the Author(s)
You May Also Like



.jpg?width=700&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=700&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=700&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)