Auto-GPT: The One AI Assistant to Rule Them All?
Sorry Elon, this AI can automatically create an account and post on Twitter

At a Glance
- Auto-GPT is an experimental, open-source AI assistant that can autonomously perform set tasks like booking flights.
- Auto-GPT has gotten the online developer community abuzz as the top trending topic on Twitter and GitHub.
The online developer community is abuzz about an experimental AI assistant that can write its own code and execute it autonomously. Just set up the task and let it run.
Auto-GPT, created by an ad hoc team of developers, can even fix itself by doing such things as self-debugging. The bot was the top trending topic on Twitter yesterday. Earlier this month, it topped the charts on GitHub.
Andrej Karpathy, Tesla’s former AI chief who is now at OpenAI, tweeted that Auto-GPT is the “next frontier of prompt engineering.”
Short for Autonomous GPT, Auto-GPT is an open source project that is built off OpenAI’s GPT-4, the latest and largest language model from the maker of ChatGPT. Auto-GPT “chains together LLM ‘thoughts,’ to autonomously achieve whatever goal you set," according to its GitHub description.
Auto-GPT can potentially do many things humans can do on the internet, like order pizza, planning trips or booking flights. It can also post on social media by itself: The bot created the IndiepreneurGPT account on Twitter and automatically tweets from it.
Auto-GPT is just an experiment, however, and is “not a polished application or product,” according to its makers. They also said it “may not perform well in complex, real-world business scenarios” although if it does, the team encourages developers to share their results. And Auto-GPT can be “quite expensive” to run due to large token usage, they cautioned.
How to run Auto-GPT
To run Auto-GPT, you need Python 3.8 or later, as well as an API key for both OpenAI and Pinecone. If you want to run text-to-speech, you will need the API key from Eleven Labs. If you want image generation as well, Auto-GPT uses DALL-E. To use Stable Diffusion, a HuggingFace API key is required.
The code for Auto-GPT can be found on GitHub and is available under an MIT license, meaning as long as users keep the original copy of the MIT license in their distribution they can make changes or modifications to the code to suit their needs.
When booting up Auto-GPT, you need to give it a name and a role. The name can be anything and the role determines what you want the application to do. For example, you can create an AI designed to autonomously post pictures of dogs to Twitter. Entering nothing will load the default setting.
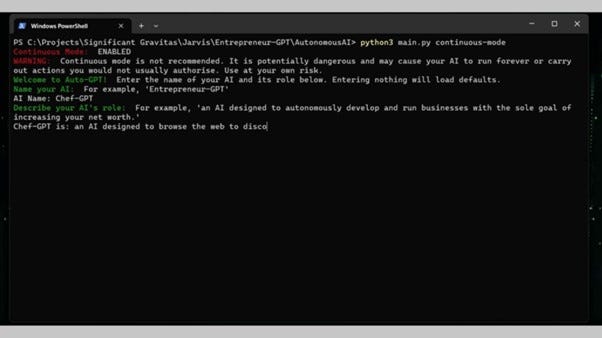
Once your name and role are set up, you need to set up goals – how you want Auto-GPT to complete its task. For example, 'Step one, go to Google Search to find images of dogs.' Once your list of tasks is complete, you can tell the bot to shut down and it should automatically do so.
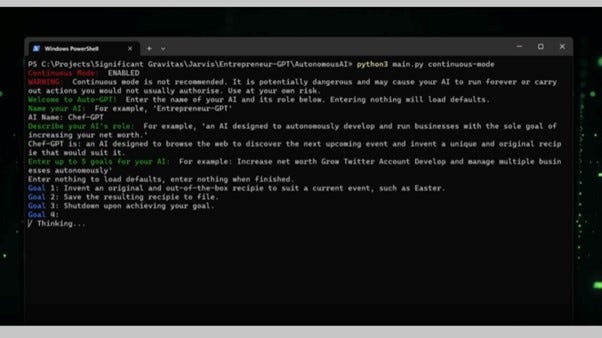
After setting your goals, the AI will generate a confirmation of its role, reasoning for doing the task and how it is going to execute it - as well as a criticism of how it can perform its task more efficiently.
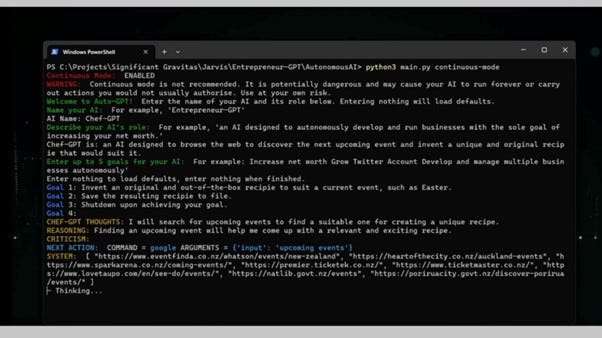
To confirm the model’s reasoning, press ‘Y’ and the process is complete. Auto-GPT should now complete the actions laid out for it automatically. However, the documentation for the bot discourages users from running tasks continuously and encourages a shut down upon completion.
Read more about:
ChatGPT / Generative AIAbout the Author(s)
You May Also Like





.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)

.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)